One of the most common full custom design types that necessitates the creation of a full custom mask package is the standard-cells based design. The polycell is another name for the standard cell. All of the commonly used logic cells are generated, characterised, and stored in a standard cell library in this design style.Inverters, NAND gates, NOR gates, complex AOI, OAI gates, D-latches, and flip-flops are among the cells found in a typical library. To provide adequate driving capability for different fanouts, each gate form may have several implementations.For example, the inverter gate may have standard, double, and quadruple size transistors, allowing the chip designer to choose the appropriate size to achieve high circuit speed and layout density. Each cell is characterised for a number of different categories.. It consists of
- delay time vs. load capacitance
- circuit simulation model
- timing simulation model
- fault simulation model
- cell data for place-and-route
- mask data
Figure-2: A simplified floorplan of standard-cells-based design.
The most difficult task is to position individual cells into rows and interconnect them in a way that meets stringent design goals in circuit speed, chip area, and power consumption after chip logic design is completed using standard cells from the library. To achieve these goals, several advanced CAD tools for place-and-route have been created and used.Circuit models with interconnect parasitics can also be extracted from the chip layout and used for timing simulation and analysis to define timing critical paths. To meet the timing criteria for critical paths, proper gate sizing is frequently used.Standard-cells-based design is used to implement complex control logic modules in many VLSI chips, such as microprocessors and digital signal processing chips. Some fully customised chips can also be built entirely out of standard cells.
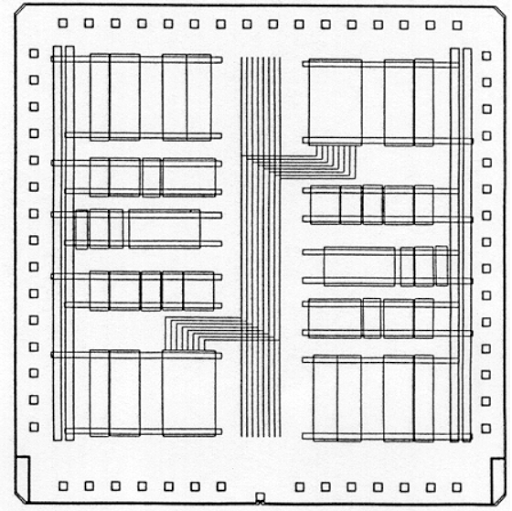
Finally, Fig. 4 depicts the complex mask layout of a standard-cell-based chip with a continuous single block of cell rows and three memory banks on one side. The separations between neighbouring rows within the cell block are determined by the number of wires in the routing channel between the cell rows.If the routing channel can reach a high interconnect density, the standard cell rows can be positioned closer together, resulting in a smaller chip region. The availability of dedicated memory blocks also decreases the amount of space required, as memory elements created with standard cells will take up more space.
Figure-4: Mask layout of a standard-cell-based chip with a single block of cells and three memory banks.



Comments
Post a Comment